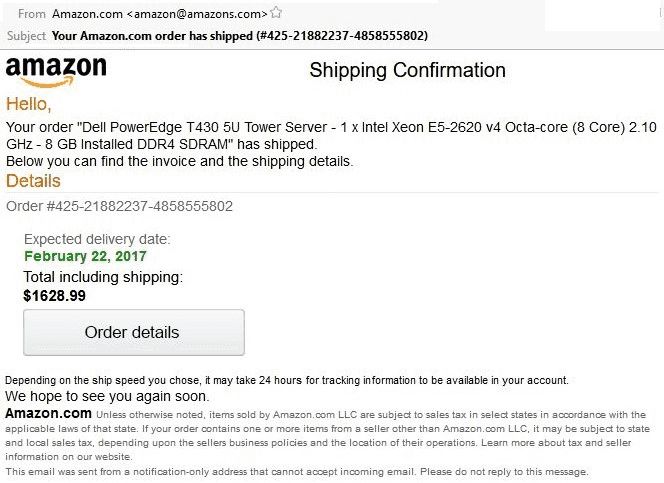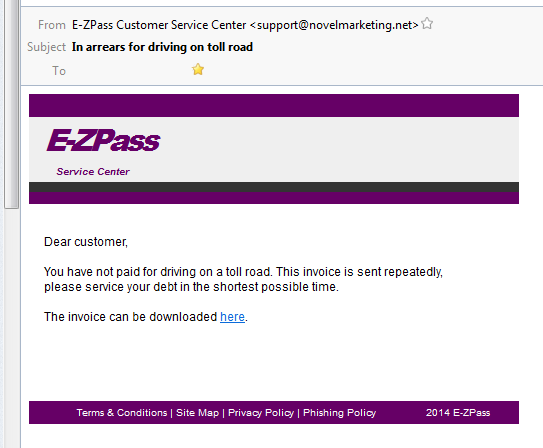
I’m often asked whether an email is real, or safe, or dangerous. And the same question shows up applied to web sites And robocalls are rampant right now, and seem to pick up around year-end. What’s real?
Short answer: If you think it’s a scam, it’s probably a scam. It’s either an attempt to have you open a software installer, or read a fake purchase order, or link to a web site selling garbage.
Scam emails have a few things in common:
- Fake urgency. Act Now! Limited Time Offer! Your computer is infected!
- False Authority. These are quotes from big-name companies and “experts” pushing whatever they’re selling. The quotes either not real, or from people who are not experts in the correct specialty.
- Fake address. The email address of the sender is from the wrong domain name.
- Poor English. Spelling, grammar, or usage are wrong. Incorrect capitalization is common.
- Jumbled. Word order is typical of languages other than English.
- Short. If there’s an attachment or a link, the message is frequently one line, because that makes it more difficult for SPAM filters to recognize a bad message.
Good emails and web sites:
- For an email, the sending email address is at the same domain as the web links. So mail ABOUT Chase Bank is FROM Chase.com, not a Gmail account.
- Have phone numbers, especially a direct-dial non-toll-free number.
- Have a physical address. Even a post office box is OK. That physical address is required by law in commercial emails, under the CAN-SPAM act.
- Emails have a WORKING Unsubscribe link, also required by law.
When in doubt, look it up:
Some of this applies to products as well; check these sites to look up the reputation of a company or a web site.
On Google.com, type in the site or product name, and ‘complaints’. Then in the results, look for companies that you know that do reviews, including any of these:
There are other review sites, but be aware that most small sites have poor moderation, and bad reviews could be from competitors. And of course, there are companies that “manage reputations” and that basically means “flood review sites with good reviews until the bad reviews are pushed off the first page.” The companies above are somewhat skilled at detecting those duplicate submissions, and these are not, but may still provide some useful information. The ‘grain of salt’ guideline applies:
For any question of “Is this file I received safe to open?” you can upload it at VirusTotal.com, and it will do multiple antivirus scans immediately.
In general, online reviews of companies or products that are a single line of text, and don’t actually mention the name of what they’re reviewing, are likely bulk submissions from a paid reputation management service. Ignore them, and read the longer reviews signed with real names, or (on some sites) marked as ‘Verified Purchaser’ or similar.
Bad emails and web sites:
- Hide their physical location. Contact, if any, is by email or chat. There is often no clue as what country they are in.
- Offer to ‘install software to allow you to view’ their page. That’s an offer to install malware. Close that page.
Both good and evil web sites have:
Encrypted web sites, with addresses starting with https. While secure web sites do provide protection from information entered into an online form from being read ‘in-traffic’ as it goes through the internet, https links do not provide confirmation of identity, just encryption. A “green padlock” link can provide identity confirmation, but only if it’s issued by a known “certificate authority”, and checking the encryption certificate for the issuer is going to show information that is mostly not easy to understand; it’s not a good indication of good or evil.
Already on a Site, and Suspicious?
High-pressure web sites tend to scroll forever, and show an auto-starting video, with no indication of length, that does not allow you to skip ahead. They’re selling the modern equivalent of snake oil, or the cure-all nostrum of the day. They’re promising something that they won’t tell you the price of until you get to the end of that video. They’ll pack that video with, again, fake urgency and endorsements from impressive experts you’ve never heard of, and it’s all just formula pressure sales that are modeled on the old in-person free seminars that push real estate investment books to anyone willing to sit through 4 hours of talking. Close that site.
“We’re from Visa/Mastercard, contacting you about lowering your rate…” Unless you are a bank, you don’t have an account with either the real MasterCard or Visa companies; you have accounts with banks. Visa and MasterCard are credit card interchange corporations, and they do business with banks, not individuals. Visa and MasterCard are competitors, and they would not co-market interest rate discounts even if they sold accounts directly.

Caller-ID is now reliably fiction. I sell phone service, as ‘voice over internet’ or VOIP, and in the setup of each user, you can type in anything you want to be visible as the caller ID information. Telemarketing phone systems change that text constantly. The newest such call here showed ‘Discover Card’ as the caller, but the computer-read script started with claiming to be from Visa/Mastercard’s security department.
Overall:
Always look at the sender’s email address. If it doesn’t match what’s claimed in the email, there’s something wrong.
Always look at link destinations before you click; just float the mouse over the link and look in the bottom-left corner of your screen for the destination. It should match the addresses and email domain.
And be suspicious. Always. The internet makes the wild, wild west look lawful and organized. At the very least, they had a local sheriff.